上海金畔生物科技有限公司为生命科学和医药研发人员提供生物活性分子抑制剂、激动剂、特异性抑制剂、化合物库、重组蛋白、同位素标记物,专注于信号通路和疾病研究领域。
Trimethylamine N-oxide-d9 (Synonyms: 三甲胺N-氧化物 d9) 纯度: ≥99.0%
Trimethylamine N-oxide-d9 是 Trimethylamine N-oxide 的氘代物。Trimethylamine N-oxide 是一种膳食胆碱和其他含三甲胺营养素的肠道微生物依赖性代谢产物。Trimethylamine N-oxide 通过激活 ROS/NLRP3 炎性体诱导炎症。Trimethylamine N-oxide 还通过激活 TGF-β/smad2 信号通路来加速成纤维细胞的分化并诱导心脏纤维化。
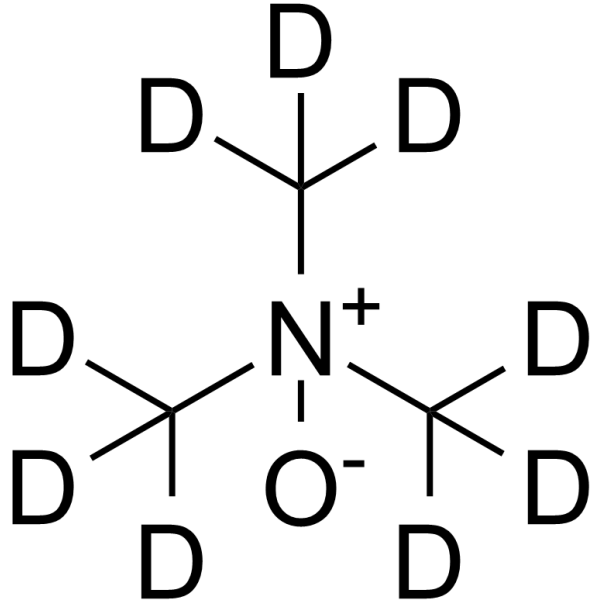
Trimethylamine N-oxide-d9 Chemical Structure
CAS No. : 1161070-49-0
| 规格 | 价格 | 是否有货 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | ¥7800 | In-stock | |
| 10 mg | 询价 | ||
| 50 mg | 询价 |
* Please select Quantity before adding items.
| 生物活性 |
Trimethylamine N-oxide-d9 is the deuterium labeled Trimethylamine N-oxide. Trimethylamine N-oxide is a gut microbe-dependent metabolite of dietary choline and other trimethylamine-containing nutrients. Trimethylamine N-oxide induces inflammation by activating the ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome. Trimethylamine N-oxide also accelerates fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation and induces cardiac fibrosis by activating the TGF-β/smad2 signaling pathway[1][2][3]. |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. Shanghai Jinpan Biotech Co Ltd has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
|||||||||
| 分子量 |
84.17 |
|||||||||
| Formula |
C3D9NO |
|||||||||
| CAS 号 |
1161070-49-0 |
|||||||||
| 中文名称 |
三甲胺N-氧化物 d9 |
|||||||||
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere. |
|||||||||
| 储存方式 |
|
|||||||||
| 参考文献 |
|
所有产品仅用作科学研究或药证申报,我们不为任何个人用途提供产品和服务
